
The proton-proton cycle is particularly slow-only one collision in about 10 26 for the cycle to start. This mass difference, known as mass defect in the parlance of nuclear physics, is converted into 26.7 MeV of energy as known from Einstein’s equation E = mc 2. The mass of the end product is 0.0475 × 10 − 27 kg less than the combined mass of the 3 He nuclei. The net result of the proton-proton cycle is that four hydrogen nuclei combine to create one helium nucleus. Consequently, they have spurred our interest in the other source of nuclear energy-fusion. The Fukushima disaster in particular has shattered the zero risk myth of power reactors and heightened our concern about the invisibility of the added lethal component, nuclear radiation. They were a sobering reminder of what we can expect from an accident due to catastrophic reactor failure or human errors. What has raised our fear in regard to nuclear power more than anything else are the accidents at Chernobyl in 1986 and Fukushima in 2011. Another area of great concern is the hazards associated with the disposal of highly radioactive waste products.
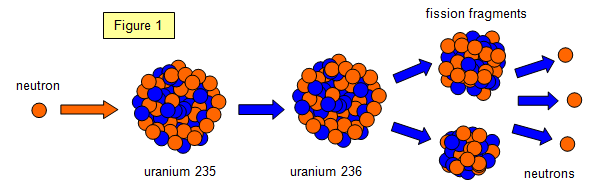
Besides, it is by no means certain that the safety systems designed to shut down the reactor in the event of a runaway reaction are 100% foolproof and will work as designed. A reactor is considered safe when a self-sustained chain reaction is maintained with exactly one neutron from each fission inducing yet another fission reaction.Ģ.2 Problems and concerns with fission reactorsĪlthough fission-based nuclear reactors generate huge amounts of electricity with zero greenhouse gas emissions, and thus was hailed as a solution not only to global warming but also to global energy needs, nuclear energy is now seen by many, and with good reasons, as the misbegotten stepchild of nuclear weapons programs. The neutrons produced in the reaction cause more fission resulting in a self-sustaining chain reaction. When 235 U is bombarded with a slow neutron, it captures the neutron to form 236 U, which undergoes fission producing two lighter fragments and releases energy together with two or three neutrons. Natural uranium contains 0.7% of the fissile 235 U the rest is non-fissile 238 U. The major improvement is the elimination of the combustion products of fossil fuels-the greenhouse gases, which have destroyed our environment beyond repair.īecause of its abundance in nature, most nuclear reactors use uranium as fuel.
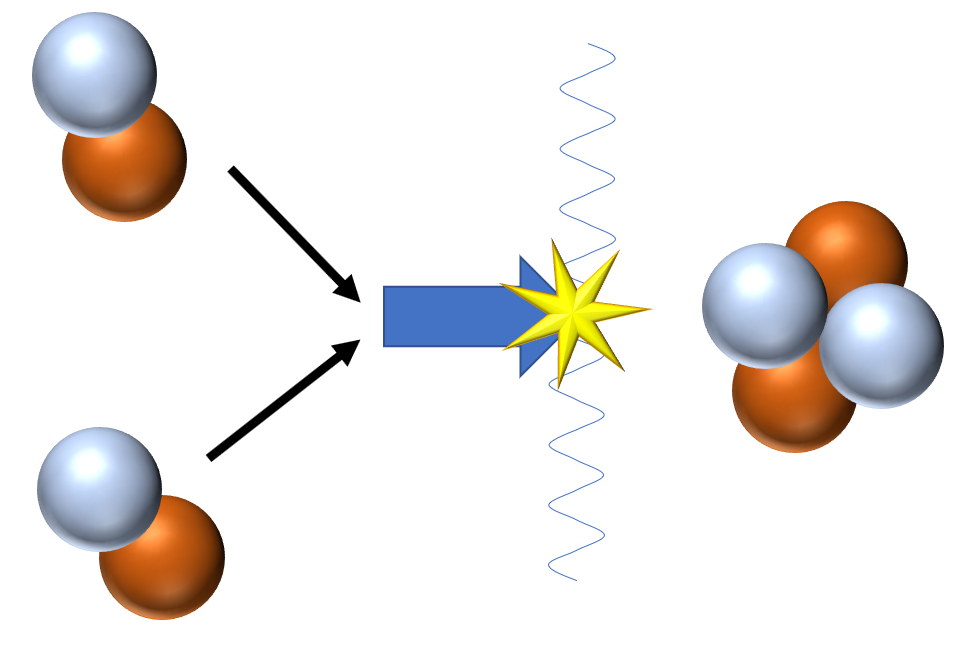
#Two nuclei combine to form one nucleus in nuclear fission. generator#
The steam turns the turbine blades, the blades generate mechanical energy, the energy runs the generator, and the generator produces electricity. Only the source of heat energy differs-nuclear power plants use fissile radioactive nucleus, while nonnuclear power plants use fossil fuel. The reactor functions primarily as an exotic heat source to turn water into pressurized steam. Emphasis is given on overcoming some of the technological challenges, such as surmounting the Coulomb barrier, confining the plasma, and achieving the “ignition” temperature for fusion.Īll nuclear power plants in operation today rely on controlled fission of the isotopes of uranium and plutonium. Various research programs dedicated to building fusion reactors are also discussed. In this chapter, harnessing the energy produced in nuclear fusion reaction in a laboratory environment is discussed. It is nuclear fusion-a process in which two lighter nuclei, typically isotopes of hydrogen, combine together under conditions of extreme pressure and temperature to form a heavier nucleus.

There is another kind of nuclear energy that has been powering the Sun and stars since their formation. However, the 1986 Chernobyl and 2011 Fukushima accidents have heightened our fears about nuclear technology’s ability to provide a safe way of generating clean power. The declining reserves of fossil fuels and their detrimental effects on the environment have thrust nuclear power based on fission reaction into the limelight as a promising option to energy-starved economies around the world.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
